The Arab Programmer's Guide to Data Structures and Algorithms
What Are Data Structures and Algorithms?
Think of data structures as ways to organize information and algorithms as recipes to solve problems with that data. For example, a family tree or a library catalog is a data structure, while searching for a specific name in the list is an algorithm. Together, these fundamental algorithms and basic data structures teach programmers to handle large data sets efficiently. In simple terms, DSA concepts are the tools that help software "think" and solve complex tasks smoothly. No matter what programming language you use -- C++, Java, Python or others -- you'll rely on these core principles to store, organize, and process data effectively.
Data Structures: Arrays, linked list implementation, stack vs queue, hash table collision resolution, tree data structure types, and graph algorithms explained are just a few examples. Each structure has its own strengths and use-cases.
Algorithms: Methods like binary search, quicksort algorithm comparison, Dijkstra's shortest-path, or dynamic programming examples. These define how we use data structures to solve problems efficiently.
Efficiency: Studying DSA also means learning about time and space complexity -- essentially, understanding algorithm performance and how much memory different approaches use.
For instance, Google Maps finding the fastest route uses advanced approaches based on Dijkstra's algorithm on a graph of roads. This real-world example shows data structures and algorithms in action: the data structure is the road network (a graph) and the algorithm efficiently computes the best path.

What is Online Learning?
Why Data Structures & Algorithms Matter for Your Career in MENA
Mastering data structures and algorithms (DSA) gives you the power to write scalable, efficient code that meets the demands of modern software development. Well-chosen approaches can drastically speed up applications and save memory—crucial in mobile app development and cloud-based platforms popular across the MENA region. This isn’t just theory; it’s what separates average code from production-ready solutions used by companies like Souq (now Amazon MENA), Careem, or fintech startups across Cairo, Riyadh, and Dubai.
Here’s why DSA is worth your time—and how it directly impacts your career:
Build Scalable, Fast Code: Algorithms help software handle growing amounts of data without slowing down. Using a hash table for quick lookups or implementing binary search instead of linear search can make e-commerce platforms or financial apps much faster—critical for millions of users across the Arab world.
Solve Real-World Problems: From optimizing traffic flow in Saudi Arabia’s NEOM smart city initiative to designing secure banking systems in the Gulf, DSA tools allow you to break down complex problems and implement the most effective solutions.
Write Optimized Code: Knowledge of algorithms in computer science helps you reduce loops, save memory, and avoid inefficiencies—key for apps that must perform well even on older devices common in emerging markets.
Ace Technical Interviews: Coding interviews across MENA—whether with regional leaders like Talabat and Careem or global tech giants—regularly test DSA knowledge. Fluency in concepts like sorting algorithms, dynamic programming, or graph shortest path solutions allows you to solve problems under pressure, explain your logic clearly, and optimize on the fly.
Perform in Coding Tests & Challenges: Many employers use online coding assessments as a first screening step. Candidates strong in DSA consistently outperform others, advancing to deeper interview rounds and better opportunities.
Excel in Competitive Programming: Hackathons and coding competitions, increasingly popular at universities in Egypt, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia, rely heavily on data structures and algorithms. Success here sharpens analytical skills and strengthens resumes for top-tier tech positions.
On-the-Job Problem Solving: DSA applies daily—from choosing efficient data structures for e-commerce recommendation systems to building AI models that process Arabic-language datasets. Even seemingly small choices, like using a tree-based index in a database, can make or break system performance.
Cross-Field Applications: Beyond software engineering, DSA is critical in data science, AI, and machine learning. Arabic NLP, for example, depends on optimized algorithms and specialized data structures to handle massive training corpora.
Stay Versatile in a Fast-Changing Industry: While technologies change, core DSA principles remain constant. Once you master them, learning new frameworks or programming languages becomes much easier, since the underlying problem-solving concepts are the same.
In short, data structures and algorithms are the backbone of computer science and modern tech careers. They make your code robust, efficient, and future-proof—whether you’re tackling a hackathon in Cairo, building fintech systems in Riyadh, or contributing to AI innovation in Dubai. As freeCodeCamp puts it, “DSA are an important aspect of any programming language and are always needed to solve complex problems.”
Common Data Structures You Should Know
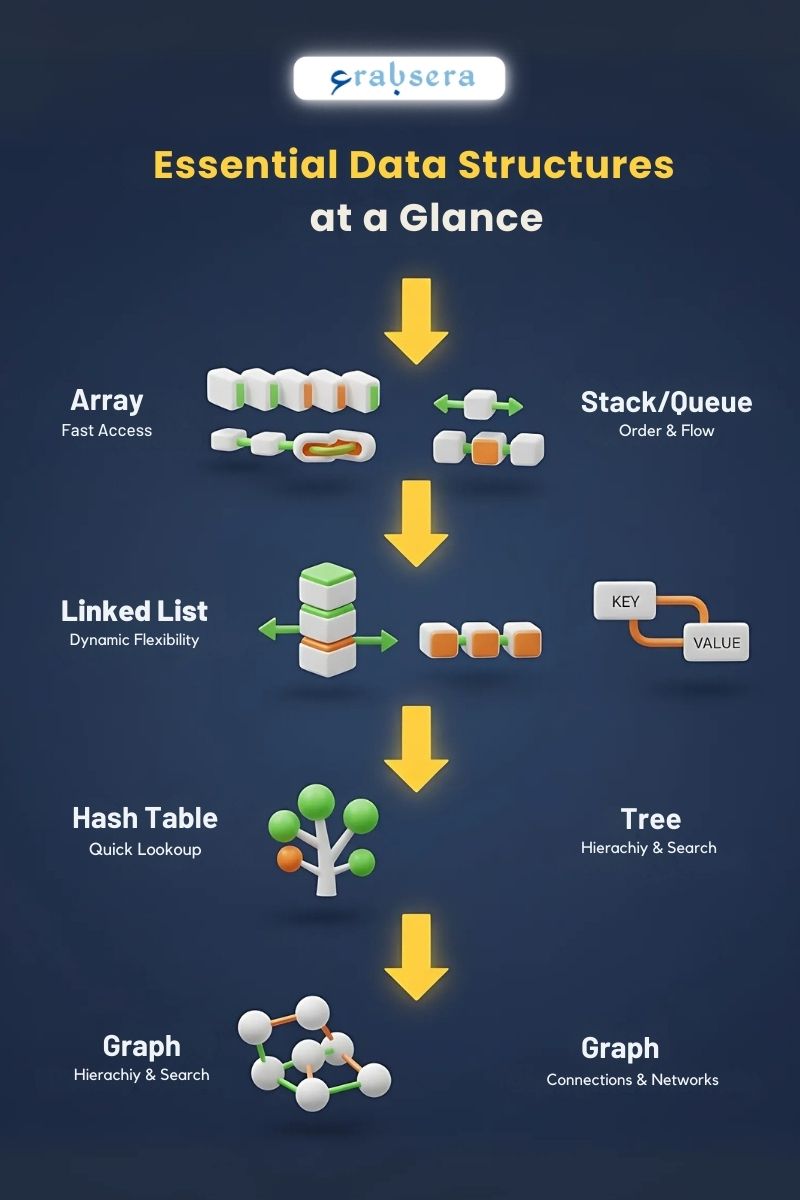
Beginners often get confused by how many different types of algorithms and data structure types exist. Let's break down the essential structures and when to use them, with examples relevant to MENA developers:
Arrays: A simple list of elements indexed by number. Use arrays when you have a fixed-size collection and need fast random access. For example, storing daily prayer times for a month across different cities in the region, or maintaining temperature readings from smart sensors in Dubai's IoT infrastructure. (However, dynamic arrays are used for varying size elements.)
Linked Lists: Items where each element points to the next. Great for fast insertions and deletions only at special locations, e.g., head and tail. Think of managing a playlist of Arabic music -- you can easily add or remove songs by relinking. This flexibility makes linked list implementation particularly useful for dynamic content management systems.
Stacks & Queues: Special lists with strict access rules. A stack (last-in, first-out) is like a pile of plates; a queue (first-in, first-out) is like a line at the bank during Eid shopping season. Use a stack for undo functionality in an Arabic text editor, or implement a queue for managing customer service requests during peak shopping periods like Ramadan.
Hash Tables (Hash Maps): Key-value stores with nearly constant lookup time when using a good hash function. Ideal for fast exact search and lookup tasks, like phone-number to customer record.
Trees: Hierarchical data structures (like family genealogies common in Arab culture). A binary search tree, for example, can maintain sorted data for fast search, insertion, or deletion. Trees are the basis for many advanced structures: balanced search trees for ordered sets/maps; B-trees/B+-trees for on-disk indexes; tries/ternary search trees (and their compressed form, DAWGs) for prefix search & autocomplete, among many others.
Graphs: Networks of nodes and edges that model relationships. They represent road networks in GPS applications for cities like Riyadh or Alexandria, social networks connecting the Arab diaspora, or dependencies between tasks in project management for construction projects like those in Qatar or UAE.
These can be linear data structures (arrays, lists, stacks, queues) or nonlinear (trees, graphs). Each has trade-offs relevant to different programming scenarios. For instance, arrays offer fast reads by index but resizing is costly -- important when dealing with large datasets from oil industry sensors or banking transactions. Understanding data structures and algorithms helps you choose the optimal approach for your specific use case. The table below compares common structures:
| Data Structure | Use Case | Example |
| Array | Random access by index, fixed size | Store monthly sales figures for retail chains across MENA |
| Linked List | Frequent inserts/deletes | Arabic music playlist (add/remove songs) |
| Stack/Queue | Controlled access (LIFO/FIFO) | Browser back-button (stack), Hajj pilgrimage queue management (FIFO) |
| Hash Table | Fast lookups by key | Customer lookup in telecom billing systems |
| Tree | Sorted/hierarchical data | Arabic language dictionary structure: use tries/ternary search trees and B/B++ trees. |
| Graph | Network relationships | Social media connections in Arab communities, shipping routes between MENA ports |
This quick comparison shows why choosing the right structure matters for solving algorithm problems effectively. Each of the above appears in programming interviews at companies across the region and real projects, so be comfortable with when and why to use them.
Key Algorithms and Their Applications
Alongside data structures, fundamental algorithms shape how we solve problems in software development. Here are some key categories and where they shine in regional contexts:
Searching Algorithms: These find items efficiently in data collections. Linear search scans each element (useful for small or unsorted data like local business listings). Binary search halves the search space each time (requires sorted data) and is much faster (O(log n) time) -- perfect for searching through large databases of Arabic content or customer records.
Sorting Algorithms: These arrange data systematically. Bubble sort and insertion sort are easy to learn (O(n²) worst-case) but slow on big data. Merge sort and quicksort are faster (O(n log n) on average) and used in production systems.. Understanding sorting algorithms comparison is crucial when processing large datasets from industries like petrochemicals or logistics common in the Gulf states.
Dynamic Programming: A powerful technique to break down complex problems into overlapping subproblems. It's used in many optimization tasks relevant to the region -- from resource allocation in oil production to route optimization for delivery services during peak seasons. DP exploits overlapping sub-problems and helps by storing results to avoid redundant calculations,
Greedy Algorithms: These make the "best" choice at each step.. They don't always work for every problem, but for some , greedy algorithms applications yield optimal solutions efficiently. For example, a word-frequency map {token → count} (after normalizing Arabic diacritics/alef/ya) tallies terms quickly without needing ordering.
Backtracking Algorithm Tutorial: Techniques for exhaustive search (like solving Sudoku puzzles popular in Arab newspapers or complex scheduling problems). You try a solution path, backtrack upon failure, and try alternatives -- essential for constraint satisfaction problems.
Graph Algorithms: BFS (breadth-first search) and DFS (depth-first search) traverse networks efficiently. These apply to social network analysis, supply chain optimization for companies operating across multiple Arab countries, and network security applications increasingly important in the region's digital transformation.
For coding interviews at tech companies establishing offices in cities like Cairo, Dubai, or Riyadh, sorting and searching are absolutely fundamental concepts you must master. You might be asked to implement binary search or explain quicksort performance characteristics. Competitive programming events, increasingly popular at universities across Egypt and Saudi Arabia, often stress graph algorithms and dynamic programming problems. Regular practice solving problems in each category builds the problem-solving skills essential for data structures and algorithms success.
Example: Consider sorting five numbers [3,1,4,1,5] -- a common interview question. A simple bubble sort will repeatedly swap neighbors (O(n²)), while merge sort will use a divide and conquer approach to sort halves (O(n log n)), then merge results. Here's a mini comparison relevant to algorithm optimization:
| Algorithm | Worst-case Time | Use Case |
| Bubble Sort | O(n²) | Educational/demo purposes, very small datasets |
| Quick Sort | O(n²) worst (rare) | General-purpose sort, average O(n log n) performance |
| Merge Sort | O(n log n) | Stable sort, reliable worst-case for large datasets |
| Binary Search | O(log n) | Fast lookup in sorted collections |
Each algorithm has its trade-offs that impact code efficiency. For example, quicksort is fast on average (O(n log n)) but will not help when data is already nearly sorted, in contrast to Timsort. Merge sort is reliable but requires extra memory. Knowing these helps you pick the right algorithm for the task and articulate your reasoning during technical interviews -- a skill highly valued by employers implementing large-scale systems across the MENA region.
Understanding Complexity: Big O Basics
A key concept in data structures and algorithms is Big O notation, which describes how an algorithm's time or space requirements grow as input size increases. This becomes particularly important when building applications that serve large populations across Arab countries. For example:
Accessing an array element is O(1) (constant time) -- ideal for real-time applications.
Binary search is O(log n) (it halves the search space each step) -- efficient for large sorted datasets.
A single loop over n items is O(n) -- linear scaling with data size.
Nested loops often lead to O(n²) -- can become problematic with large datasets.
Time complexity dictates how well your code scales when serving millions of users across the MENA region, and space complexity tells you memory requirements -- crucial for mobile apps running on diverse device specifications. These concepts ensure that, as your data grows from serving local markets to regional or global audiences, you choose solutions that won't suddenly become impractical. Whenever you learn a new approach in data structures and algorithms, always ask, "What's the Big O?" -- and compare it to alternatives. It's the core of achieving optimal performance in software systems.
Overcoming DSA Challenges
It's normal to struggle with fundamental algorithms and data structures concepts at first, especially for students whose primary education was in Arabic but who are learning programming in English. Many beginners feel it's like learning a new language -- and in a way, it is. You're learning new patterns of computational thinking. Here are culturally-aware tips to overcome common hurdles:
Avoid the "Volume" Trap: Don't just solve hundreds of coding problems blindly. Focus on understanding each data structures and algorithms concept thoroughly. Master one structure or algorithm, then move on -- quality over quantity is key to building solid foundations.
Practice in Context: Instead of memorizing formulas, work through examples relevant to your experience. Build a linked list by hand, code a simple sort in your preferred language, or simulate graph traversal on paper using familiar networks like family connections or regional trade routes.
Build Intuitions: Use analogies from daily life (a queue is like a line at the mosque during Friday prayers, a stack is like organizing documents in an office). Visualize how data moves through different structures. This makes complex ideas (like recursion or pointer manipulation) much clearer for learners from diverse educational backgrounds.
Structured Learning Path: Follow a step-by-step roadmap that builds knowledge systematically. Start with basics (arrays, pointers), then advance to more sophisticated topics (trees, graphs, dynamic programming). A well-designed course that understands the learning challenges faced by Arab students can guide you through this progression. Arabsera's data structures and algorithms courses, for instance, break topics into manageable modules with hands-on examples and bilingual explanations.
Regular Practice: DSA skills improve with consistent repetition and application. Set aside daily or weekly coding time that fits your schedule (considering cultural and religious observances). Use platforms like HackerRank, LeetCode, or local coding communities to solve problems, and review discussions to learn different approaches to implementing fundamental algorithms.
Focus on Understanding, Not Memorization: It's tempting to memorize solutions to common problems, but technical interviews often present variations that require deep understanding. Understand why an algorithm works and how data structures support efficient operations. If you grasp the underlying logic of different types of algorithms, you can adapt to new challenges confidently.
Ask Questions and Collaborate: Learning with peers or mentors accelerates progress significantly. Participate in study groups at local universities like American University of Cairo, King Fahd University, or online communities. At Arabsera, we encourage discussion and Q&A sessions to help students clarify doubts about data structures and algorithms early in their learning journey.
By tackling DSA systematically this way, what once seemed impossibly complex becomes manageable and even enjoyable. Remember: even experienced engineers at companies like Noon.com or Fetchr constantly practice and refine their understanding of algorithms and data structures. It's a skill that grows over time with dedicated effort. Don't get discouraged by early difficulties -- every expert was a beginner once, and the strong problem-solving culture in Arab education systems actually provides excellent preparation for mastering these concepts.
How Arabsera Can Help You Master DSA
At Arabsera (a leading bilingual STEM education platform serving the Arab world), we understand the unique challenges students face when learning complex technical concepts. That's why our comprehensive Data Structures & Algorithms Course is specifically designed to make mastering these fundamental programming concepts both accessible and practical for Arabic-speaking learners. Here's what sets our culturally-aware approach apart:
Expert Instructors: Learn from experienced computer science educators and industry professionals who have worked at major tech companies across MENA. They explain data structures and algorithms concepts in clear, culturally-relevant language that resonates with Arab learners.
Bilingual Content: We specifically cater to Arabic-speaking students by offering comprehensive explanations and practical examples in both Arabic and English, bridging the significant gap in existing educational resources and making complex algorithmic concepts accessible in your native language.
Hands-on Examples: Each topic covering everything from basic data structures to advanced dynamic programming examples is accompanied by real code implementations and interactive visualizations. For instance, when we teach binary search implementation, we show step-by-step illustrations of how the search zone efficiently halves each time.
Structured Roadmap: Our carefully designed curriculum follows a proven learning path (eliminating the confusion of jumping between random tutorials). We systematically start with fundamentals like arrays and simple sorting algorithms, then build up to sophisticated topics including graph algorithms and advanced optimization techniques.
Interactive Practice: Extensive practice problems and quizzes help reinforce learning of key data structures and algorithms concepts. Get immediate feedback and contextual hints to correct mistakes early, with problems specifically chosen to reflect real-world scenarios relevant to the MENA tech industry.
Supportive Community: Join a vibrant community of fellow learners from across the Arab world. Ask questions in Arabic or English, receive mentorship from experienced developers, and collaborate on solving challenging algorithmic problems with peers who share similar cultural and educational backgrounds.
Flexible Learning: Access comprehensive course materials anytime, anywhere -- perfect for busy students balancing studies with cultural obligations or professionals working in the demanding tech sectors of major MENA cities.
Investing your time in mastering data structures and algorithms is an investment in your long-term career success in the rapidly growing Arab tech sector. It gives you the confidence to tackle complex coding tasks and demonstrates to employers that you have a solid technical foundation. As you've seen, understanding these concepts is crucial for writing high-quality, production-ready code, and it's a standard requirement for software engineering roles across the MENA region.
Are you ready to build efficient, scalable code, solve complex problems like a seasoned professional, and unlock exciting opportunities at top tech companies expanding across the MENA region? Then take the decisive next step in your programming journey. Enroll in Arabsera's comprehensive Data Structures & Algorithms course today. Start learning with Arabsera—your trusted partner in mastering essential computer science skills and advancing your career in the thriving Arab tech ecosystem.
